ML Aggarwal Class 8 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A number ending in ……… is never a perfect square.
(ii) On combining two consecutive triangular number, we get a ………
(iii) If a number has digits ……… in the unit’s place, then its square ends in 1.
(iv) Sum of the first 10 odd natural numbers is ………
(v) A number of non-square numbers between 112 and 122 is ………
(vi) Number of zeros in the end of the square of 400 is ………
(vii) Square of any ……… number can be expressed as the sum of two consecutive natural numbers.
(viii)For a natural number m > 1, (2m, m2 – 1, m2 + 1) is called ………
Solution:

Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) All-natural numbers are not perfect squares.
(ii) A perfect square can never be expressed as the product of pairs of equal prime factors.
(iii) A number having 2,3,7 or 8 at its unit place is never a square number.
(iv) A number having 0, 1, 4, 5, 6 or 9 at its unit place is always a square number.
(v) A number ending in an even number of zeros is always a perfect square.
(vi) Square of an odd number is always an odd number.
(vii) 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, are called triangular numbers.
(viii)There are 2n non-square numbers between the squares of consecutive numbers n and (n + 1).
(ix) (4, 6, 8) is a Pythagorean triplet.
Solution:

Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (3 to 15):
Question 3.
How many natural numbers lie between 252 and 262?
(a) 49
(b) 50
(c) 51
(d) 52
Solution:

Question 4.
Square of an even number is always
(a) even
(b) odd
(c) even or odd
(d) none of these
Solution:

Question 5.
1+ 3 + 5 + 7 + ……….. up to n terms is equal to
(a) n2 – 1
(b) (n + 1)2
(c) n2 + 1
(d) n2
Solution:

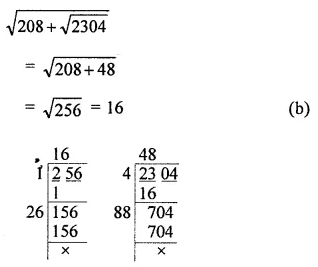
Question 6.
\(\sqrt{208+\sqrt{2304}}\) is equal to
(a) 18
(b) 16
(c) 14
(d) 22
Solution:
Question 7.
\(\sqrt{0.0016}\) is equal to
(a) 0.04
(b) 0.004
(c) 0.4
(d) none of these
Solution:

Question 8.
The smallest number by which 75 should be divided to make it a perfect square is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Solution:

Question 9.
\(\sqrt{3 \frac{6}{25}}\) is equal to

Solution:

Question 10.
The smallest number by which 162 should be multiplied to make it a perfect square is
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1
Solution:

Question 11.
If the area of a square field is 961 unit2, then the length of its side is
(a) 29 units
(b) 41 units
(c) 31 untis
(d) 39 units
Solution:

Question 12.
The smallest number that should be subtracted from 300 to make it a perfect square is
(a) 11
(b) 12
(c) 13
(d) 14
Solution:

Question 13.
If one number of the Pythagorean triplet is 6, then the triplet is
(a) (4, 5, 6)
(b) (5, 6, 7)
(c) (6, 7, 8)
(d) (6, 8, 10)
Solution:

Question 14.
nth triangular number is

Solution:

Question 15.
Given that \(\sqrt{1521}\) = 39, the value of \(\sqrt{0.1521}+\sqrt{15.21}\) is
(a) 42.9
(b) 4.29
(c) 3.51
(d) 35.1
Solution:

Value Based Questions
Question 1.
In a school, students of class VIII collected ₹9216 to give a donation to an NGO working for the education of poor children. If each student donated as many rupees as the number of students in class VIII. Find the number of students in class VIII.
Why should we donate money for the education of poor children? What values are being promoted?
Solution:

Question 2.
A person wants to plant 2704 medicinal plants with a board depicting the diseases in which that can be used. He planted these in the form of rows. If each row contains as many plants as the number of rows, then find the number of rows.
Why should we plant medicinal plants? What values are being promoted?
Solution:

Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots)
Question 1.
A square field is to be ploughed. Ramu get it ploughed in ₹34560 at the rate of ₹15 per sq. m. Find the length of side of square field.
Solution:

Question 2.
Lalit has some chocolates. He distributed these chocolates among 13 children in such a way that he gave one chocolate to first child, 3 chocolates to the second child, 5 chocolates to third and so on. Find the number of chocolates Lalit had.
Solution:




































































































































































































